 |
Sialic acids are attached to glycan chains through α-glycosidic linkages. In chemical synthesis, stereoselective α-sialylation is difficult to achieve (Fig. 1A). To obtain α-sialosides, nucleophilic attack by the hydroxy group of the glycosyl acceptor must be directed to the α-face of the oxocarbenium ion intermediate generated from the sialic acid donor. However, due to the C3-deoxy structure of sialic acid, stereocontrol by the neighboring group participation is difficult. In addition, the electrophilic carboxy group destabilizes the oxocarbenium ion intermediate and promotes 1,2-elimination (1). To overcome these problems, various α-sialylation methods have been investigated.
α-Sialylation methods can be broadly divided into nitrile solvent-dependent and nitrile solvent-independent methods. The use of nitrile as a solvent preferentially produces a β-glycosyl nitrilium ion (due to the anomeric effect), which subsequently undergoes an Sɴ2-like reaction with the hydroxy group of the glycosyl acceptor, thereby producing α-sialosides (2) (Fig. 1B). Chemical modifications of the sialic acid donors (e.g., leaving groups and protecting groups of the C5-amino group) improve the stereoselectivity and yield of nitrile solvent-dependent α-sialylation (1). On the other hand, for nitrile solvent-independent methods, sialyl donors such as C1- or C3-modified donors (1,3) and 4O,5N-oxazolidinone donors have been developed (4) (Fig. 1C). These advancements in α-sialylation described above can facilitate the chemical synthesis of sialoglycans.
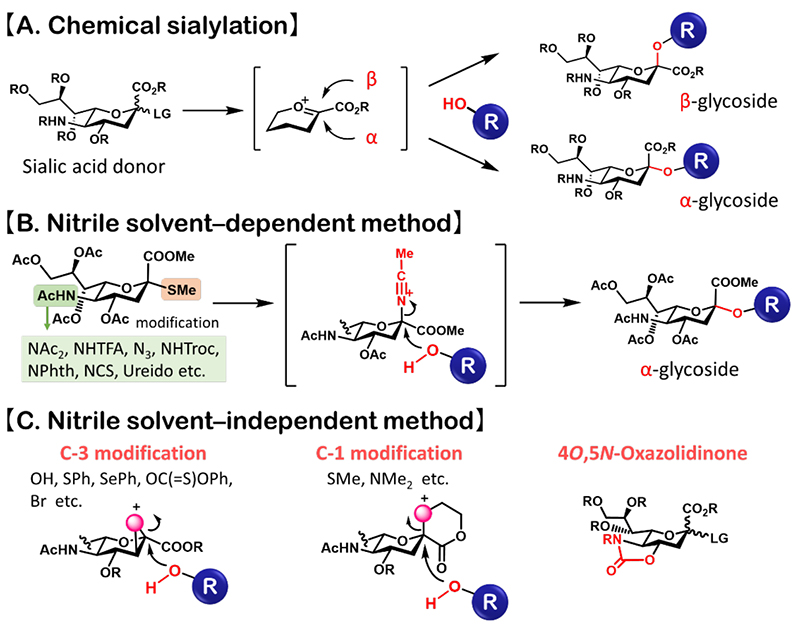
Figure 1
|
Despite the advancements described above, there is still a possibility of β-glycoside formation. Separation of stereoisomers via common purification methods is often difficult. Thus, the formation of β-glycosides can be a critical problem in the synthesis of sialoglycans. To overcome this issue, we designed a macrobicyclic sialyl donor, in which the C1 and C5 positions were tethered by an alkyl linker. We envisaged that in the glycosidation of the macrobicyclic donor, the tether moiety would completely block the β-face of the oxocarbenium ion intermediate, resulting in the formation of only α-glycoside (Fig. 2). Because the generation of the oxocarbenium ion at the bridgehead anomeric position would be unfavorable due to the ring strain (Bredt’s rule), we determined the proper tether length to allow the formation of the oxocarbenium ion at the anomeric position. The highest yield of α-glycoside with complete stereoselectivity was obtained using a 16-membered ring bicyclic sialic acid donor. With a shorter tether length, the bicyclic sialic acid donor was less reactive due to the strong ring strain; conversely, with a longer tether length, the 1,2-elimination side reactions were more likely to proceed. Furthermore, the reactivity of the 16-membered ring bicyclic sialyl donor was greatly enhanced by Cl substitutions on the tether moiety. Therefore, this method achieved fully stereoselective α-sialylation (5). Since stereocontrol of sialylation is a challenge in the automated synthesis of sialoglycans, further applications of this methodology are expected to lead to advances in sialoglycan synthesis.
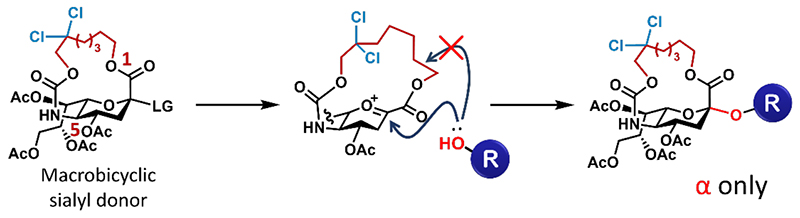
Figure 2
|
Komura Naoko
(Institute for Glyco-core Research (iGCORE), Gifu University)
| References |
| (1) |
Vibhute AM, Komura N, Tanaka HN, Imamura A, Ando H: Advanced chemical methods for stereoselective sialylation and their applications in sialoglycan syntheses. Chem. Rec. 21, 3194–3223, 2021 |
| (2) |
Kanie O, Kiso M, Hasegawa A: Glycosylation using methylthioglycosides of N-acetylneuraminic acid and dimethyl(methylthio)sulfonium triflate. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 7, 501–506, 1988 |
| (3) |
Ito Y, Numata M, Sugimoto M, Ogawa T: Synthetic studies on cell-surface glycans. 65. Highly stereoselective synthesis of ganglioside GD3. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 111, 8508–8510, 1989 |
| (4) |
Tanaka H, Nishiura Y, Takahashi T: Stereoselective synthesis of oligo-α-(2,8)-sialic acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 7124–7125, 2006 |
| (5) |
Komura N, Kato K, Udagawa T, Asano S, Tanaka HN, Imamura A, Ishida H, Kiso M, Ando H: Constrained sialic acid donors enable selective synthesis of α-glycosides. Science 364, 677–680, 2019 |
Jul. 17, 2024
|
|---|








