 |
The Golgi N-glycan processing pathway in metazoans
generates structural complexity on mature glycoproteins, in large part
due to variable numbers of N-acetyllactosamine units. These sequences
bind to galectins, a family of soluble N-acetyllactosamine-binding proteins
with either 1 or 2 carbohydrate recognition domain (CRD). Galectin affinities
for N-glycans are proportional to GlcNAc-branching and the number of N-acetyllactosamine
units (1). The highest affinity ligands are tetra-antennary products
of 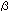 1,6
N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase V (Mgat5) extended with poly N-acetyllactosamine. 1,6
N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase V (Mgat5) extended with poly N-acetyllactosamine.
The oncogene pathway Ras-Erk-Ets stimulates Mgat5 transcription, and carcinomas
commonly display increased 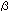 1,6GlcNAc-branching
and poly N-acetyllactosamine. Galectin-3 cross-links Mgat5-modified N-glycans
on EGF and TGF- 1,6GlcNAc-branching
and poly N-acetyllactosamine. Galectin-3 cross-links Mgat5-modified N-glycans
on EGF and TGF-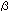 receptors at the cell surface, forming a lattice that delays receptor
removal by constitutive endocytosis (2). Galectin-3 has a single
CRD and the non-lectin N-terminal domain mediates pentamer formation in
the presence of multivalent ligands, and thereby cross-linking glycoproteins
in proportion to ligand concentrations (3). Oncogenic signaling
down-stream of receptor tyrosine kinases promotes vesicular trafficking
and endocytosis, but the concomitant increases in GlcNAc-branching of
N-glycans on receptors promotes cross-linking by galectins, and inhibits
receptor loss to endocytosis. Therefore the lattice ensures up-regulation
of surface cytokine receptors and increased sensitivity to growth factors,
in the face of increased membrane and cytoskeletal remodeling which drives
cell motility and invasion. Mammary tumor cells from Mgat5-/-
display a global loss of sensitivity to cytokines including EGF, IGF-1,
PDGF, FGF and TGF-
receptors at the cell surface, forming a lattice that delays receptor
removal by constitutive endocytosis (2). Galectin-3 has a single
CRD and the non-lectin N-terminal domain mediates pentamer formation in
the presence of multivalent ligands, and thereby cross-linking glycoproteins
in proportion to ligand concentrations (3). Oncogenic signaling
down-stream of receptor tyrosine kinases promotes vesicular trafficking
and endocytosis, but the concomitant increases in GlcNAc-branching of
N-glycans on receptors promotes cross-linking by galectins, and inhibits
receptor loss to endocytosis. Therefore the lattice ensures up-regulation
of surface cytokine receptors and increased sensitivity to growth factors,
in the face of increased membrane and cytoskeletal remodeling which drives
cell motility and invasion. Mammary tumor cells from Mgat5-/-
display a global loss of sensitivity to cytokines including EGF, IGF-1,
PDGF, FGF and TGF-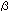 .
This results in suppression of metastasis in vivo (4), and
failure of mammary tumors to undergo epithelial-mesenchymal transition
(EMT)(2). EMT characterizes the invasive phenotype and is dependent
on activation of Ras and TGF- .
This results in suppression of metastasis in vivo (4), and
failure of mammary tumors to undergo epithelial-mesenchymal transition
(EMT)(2). EMT characterizes the invasive phenotype and is dependent
on activation of Ras and TGF-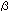 /Smad
signaling pathways. Peritoneal macrophages provide another example of
a motile and highly endocytic cell that require the galectin lattice.
Mgat5-/- macrophages are deficient for cytokine-mediated signaling,
phagocytosis, and extravasation in vivo. Galectin-3 deficient macrophages
display similar functional defects. The functional redundancy of galectin(s),
the diversity of N-glycan ligands and the multiplicity of N-glycan chains
per receptor should provide robustness to the lattice model of regulation. /Smad
signaling pathways. Peritoneal macrophages provide another example of
a motile and highly endocytic cell that require the galectin lattice.
Mgat5-/- macrophages are deficient for cytokine-mediated signaling,
phagocytosis, and extravasation in vivo. Galectin-3 deficient macrophages
display similar functional defects. The functional redundancy of galectin(s),
the diversity of N-glycan ligands and the multiplicity of N-glycan chains
per receptor should provide robustness to the lattice model of regulation.
|
|
|
It remains to be determined whether regulation of cytokine receptors
by galectins is required during embryogenesis. However, it is clear
that complex-type N-glycans containing N-acetyllactosamine are required,
as their complete absence in Mgat1-deficient mouse embryos is lethal
(5). A deficiency in Mgat2 causes reduced N-acetyllactosamine-content
in N-glycans, and a postpartum lethality in mice, and morphogenic
defects in multiple tissues similar to type II CDG disease in humans.
Postpartum lethality is also observed with deficiencies in the major
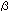 1,4Gal-T
activity (TI), one of 6 genes encoding this activity. Mgat5 is not
required for mouse embryogenesis, but adult Mgat5-/- mice
display multiple phenotypes including susceptibility to autoimmune
disease and suppression of cancer progression; both appear to be galectin-lattice
dependent phenotypes (4, 6). 1,4Gal-T
activity (TI), one of 6 genes encoding this activity. Mgat5 is not
required for mouse embryogenesis, but adult Mgat5-/- mice
display multiple phenotypes including susceptibility to autoimmune
disease and suppression of cancer progression; both appear to be galectin-lattice
dependent phenotypes (4, 6).
|
|
|
James W. Dennis1,2,3.
1. Samuel Lunenfeld Research Institute, Mount Sinai Hospital
2. Department of Medical Genetics & Microbiology, University of Toronto
3. Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology, University of Toronto
|
|
|
| References |
(1) |
Hirabayashi J, Hashidate T, Arata Y, Nishi N, Nakamura T, Hirashima
M, Urashima T, Oka T, Futai M, Muller WE, Yagi F, Kasai K: Oligosaccharide
specificity of galectins: a search by frontal affinity chromatography,
Biochim.Biophys.Acta, 1572, 232-254, 2002 |
|
(2) |
Partridge EA, Le Roy C, Di Guglielmo GM, Pawling J, Cheung P,
Grabnovsky M, Nabi IR, Wrana JL, Dennis JW: Regulation of cytokine
receptors by Golgi N-glycan processing and endocytosis. Science,
306, 120-124, 2004 |
|
(3) |
Ahmad N, Gabius HJ, Andre S, Kaltner H, Sabesan S, Roy R, Liu
B, Macaluso F, Brewer CF: Galectin-3 precipitates as a pentamer
with synthetic multivalent carbohydrates and forms heterogeneous
cross-linked complexes. J.Biol.Chem. 279, 10841-10847,
2003 |
|
(4) |
Granovsky M, Fata J, Pawling J, Muller WJ, Khokha R, Dennis JW:
Suppression of tumor growth and metastasis in Mgat5-deficient mice.
Nature Med. 6, 306-312, 2000 |
|
(5) |
Lowe JB, Marth JD: A genetic approach to Mammalian glycan function.
Annu.Rev.Biochem. 72, 643-691, 2003 |
|
(6) |
Demetriou M, Granovsky M, Quaggin S, Dennis JW: Negative regulation
of T-cell activation and autoimmunity by Mgat-5 N-glycosylation,
Nature, 409, 733-739, 2001 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|



